DDR4 Overview
Print page mac. Nov 11, 2016.
- May 19, 2016.
- Dec 06, 2019.
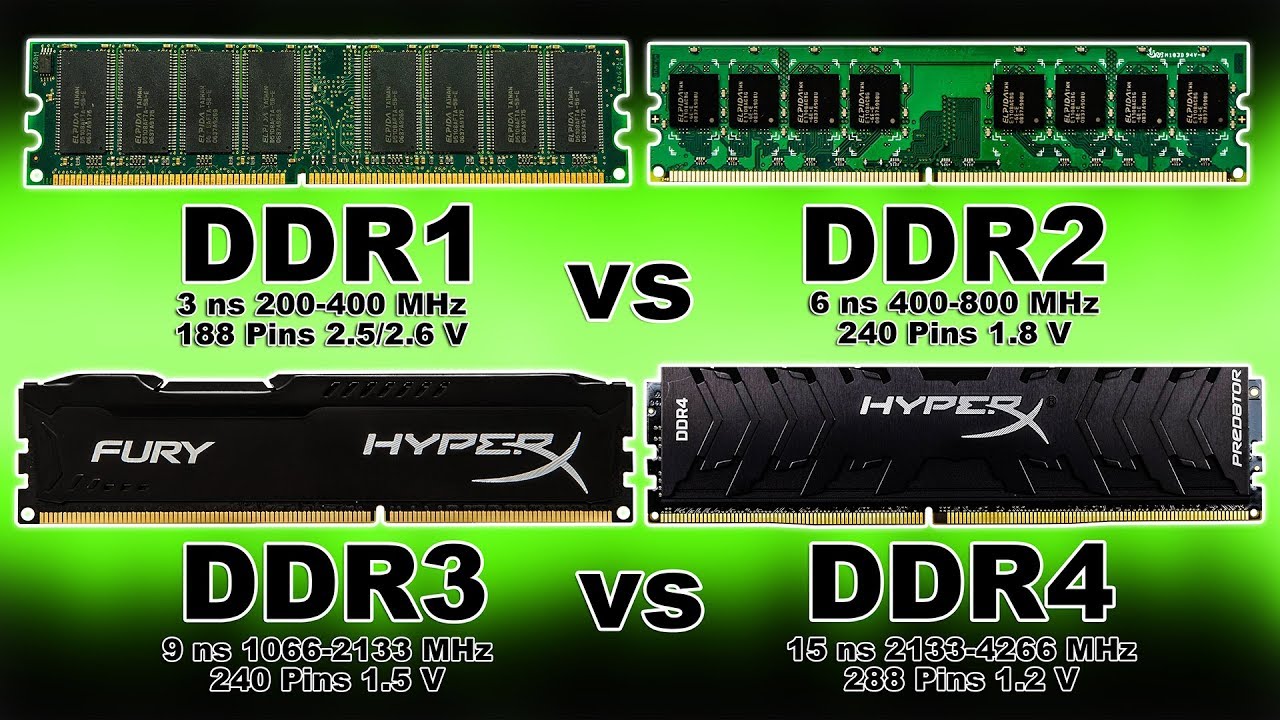
The specifications and differences between, DDR2, DDR3, DDR4 and DDR5 RAM.RAM is a form of data storage available in computers which stores data and machine code that is currently being used. DDR3 DDR4; 1. DDR3 stands for Double Data Rate version 3. Whereas DDR4 stands for Double Data Rate version 4. The cost of DDR3 is less than DDR4. While it's cost is higher or more than DDR3. In DDR3, auto-refresh and self-refresh are performed to refresh its content. While in DDR4, only self-refresh is performed to refresh its content.
Use Ddr4 In Ddr3 Slot
Pokemon black 2 rom zip. With DDR3 reaching its limits in a world that demands higher performance and increased bandwidth, a new generation of DDR SDRAM has arrived. DDR4 delivers higher performance, higher DIMM capacities, improved data integrity and lower power consumption.
Achieving more than 2Gbps per pin and consuming less power than DDR3L (DDR3 Low Voltage), DDR4 provides up to 50 percent increased performance and bandwidth while decreasing the power consumption of your overall computing environment. This represents a significant improvement over previous memory technologies and a power savings up to 40 percent
2017 ford sport trac electrical repair manual. In addition to optimized performance and greener, low-cost computing, DDR4 also provides cyclic redundancy checks (CRC) for improved data reliability, on-chip parity detection for integrity verification of ‘command and address' transfers over a link, enhanced signal integrity and other robust RAS features.
DDR4 Details
Trickster 34 oz spinnerbait. Please note that there are subtle differences between DDR3 and DDR4 modules.
Key notch difference
The key notch on a DDR4 module is in a different location from the key notch on a DDR3 module. Both notches are located on the insertion edge but the notch location on the DDR4 is slightly different, to prevent it the module from being installed into an incompatible board or platform. Clone wars nose art.
Increased thickness
DDR4 modules are slightly thicker than DDR3, to accommodate more signal layers.
Increased thickness
DDR4 modules are slightly thicker than DDR3, to accommodate more signal layers.
Curved edge
DDR4 modules feature a curved edge to help with insertion and alleviate stress on the PCB during memory installation.
Will Ddr4 Fit Ddr3
Specifications at a Glance
Ddr4 In Ddr3 Slot
| Description | DDR3 | DDR4 | Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chip Densities | 512Mb-8Gb | 4Gb-16Gb | Larger DIMM Capacities |
| Data Rates | 800Mb/s – 2133Mb/s | 1600Mb/s – 3200Mb/s | Migration to Higher-Speed I/O |
| Voltage | 1,5V | 1,2V | Reduced Memory Power Demand |
| Low Voltage Standard | Yes (DDR3L at 1.35V) | Anticipated at 1.05V | Memory Power Reductions |
| Internal Banks | 8 | 16 | More Banks |
| Bank Groups (BG) | 0 | 4 | Faster Burst Accesses |
| VREF inputs | 2 – DQs and CMD/ADDR | 1 – CMD/ADDR | VREFDQ Now Internal |
| tCK – DLL Enabled | 300MHz – 800MHz | 667MHz – 1,6GHz | Higher Data Rates |
| tCK – DLL Disabled | 10MHz – 125MHz (optional) | Undefined to 125MHz | DLL-off now fully supported |
| Read Latency | AL + CL | AL + CL | Expanded Values |
| Write Latency | AL + CWL | AL + CWL | Expanded Values |
| DQ Driver (ALT) | 40 Ω | 48 Ω | Optimal for PtP Applications |
| DQ Bus | SSTL15 | POD12 | Less I/O Noise and Power |
| RTT Values (in Ω) | 120, 60, 40, 30, 20 | 240, 120, 80, 60, 48, 40, 34 | Support for Higher Data Rates |
| RTT Not Allowed | READ Bursts | Disables during Read Bursts | Ease-of-Use |
| ODT Modes | Nominal, Dynamic | Nominal, Dynamic, Park | Add'l Control Mode; OTF Value Change |
| ODT Control | ODT Signaling Required | ODT Signaling NOT Required | Ease of ODT Control; Allows Non-ODT Routing, PtP Apps |
| Multi-Purpose Register | Four Registers – 1 Defined, 3 RFU | Four Registers – 3 Defined, 1 RFU | Provides Additional Specialty Readout |
| DIMM Types | RDIMM, LRDIMM, UDIMM, SODIMM | RDIMM, LRDIMM, UDIMM, SODIMM | |
| DIMM Pins | 240 (R, LR, U); 204 (SODIMM) | 288 (R, LR, U); 260 (SODIMM) | |
| RAS | ECC | CRC, Parity, Addressability, GDM | More RAS features; improved data integrity |
